Gynecomastia, a condition where men produce excess breast tissue, results in a feminized chest and is associated with psychological and emotional distress. It is important to evaluate for medical causes of gynecomastia and this is often performed with the assistance of a primary care physician. Some cases are self-resolving particularly in children, but in other cases, it persists into adulthood. Weight gain can worsen the appearance of gynecomastia.
In these cases, surgical intervention is the standard of care. Candidates for surgery are men who are not satisfied with the appearance of their breasts. It is best for young adults to reach complete growth before surgery because the condition may resolve on its own once hormone levels normalize and any further growth after the procedure may lead to a revision procedure.
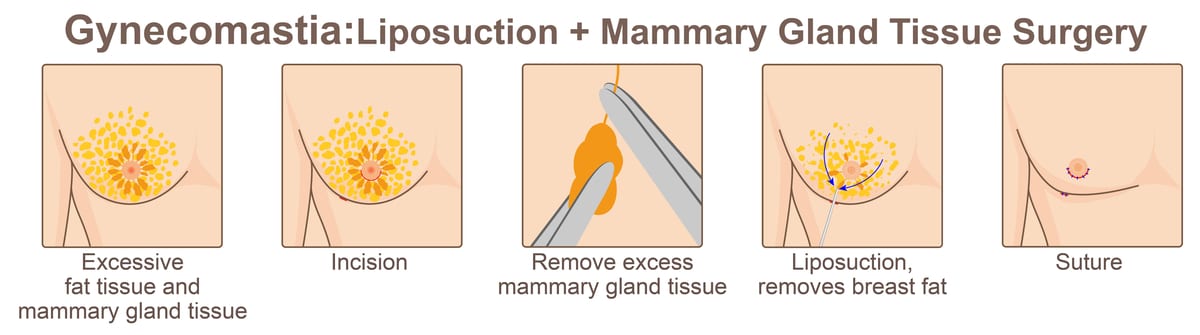
Because the fatty: breast tissue ratio is different in every patient, each patient should be evaluated and a specific treatment plan formulated. The surgical technique can range from liposuction alone vs direct excision vs a combination of both. In patients who have experienced massive weight loss, excess skin may need to be removed and the nipples repositioned on the chest. Surgery time can range from 2-4 hours depending on the technique used and the size of the breasts. Recovery time is typically 3-4 weeks although most patients return to work sooner.




